The article is about “Biochemistry Analyzer Uses and Principle“. The article will teach you fundamental knowledge about “Biochemistry Analyzer Uses and Principle” for precise diagnosis and advanced laboratory testing.
Biochemistry Analyzer Uses: Applications of Biochemistry Analyzer
Ever wonder how medical professionals determine what’s happening within our bodies? They make use of a unique device known as a biochemistry analyser.
By evaluating our blood and other bodily fluids, this incredible equipment assist doctors in obtaining essential details. It can, for instance, evaluate the level of sugar in our blood or assess the health of our liver. These are a few biochemistry analyzer uses.
The mechanism of the biochemistry analyser is also really cool! It measures the amount of light absorbed by the samples by shining light through them. This makes it easier in its determination of the various chemical concentrations within our bodies.
- Biochemistry Analyzer Uses: Applications of Biochemistry Analyzer
- What is the Working Principle of Biochemistry Analyzer?
- How Does Biochemistry Analyzer Work?
- How Many Types of Analyzers Are There in Biochemistry?
- What Are The Parts Of Biochemistry Analyzer?
- What Is The Basic Function Of Biochemistry Analyser?
- Which Biochemistry Analyser Is Best?
- Challenges and Limitations of Biochemistry Analyzers Use
What is a Biochemistry Analyzer?
An essential piece of instrument used in medical labs is a biochemistry analyser, which is made for analysing the chemical composition of different body fluids, particularly blood.
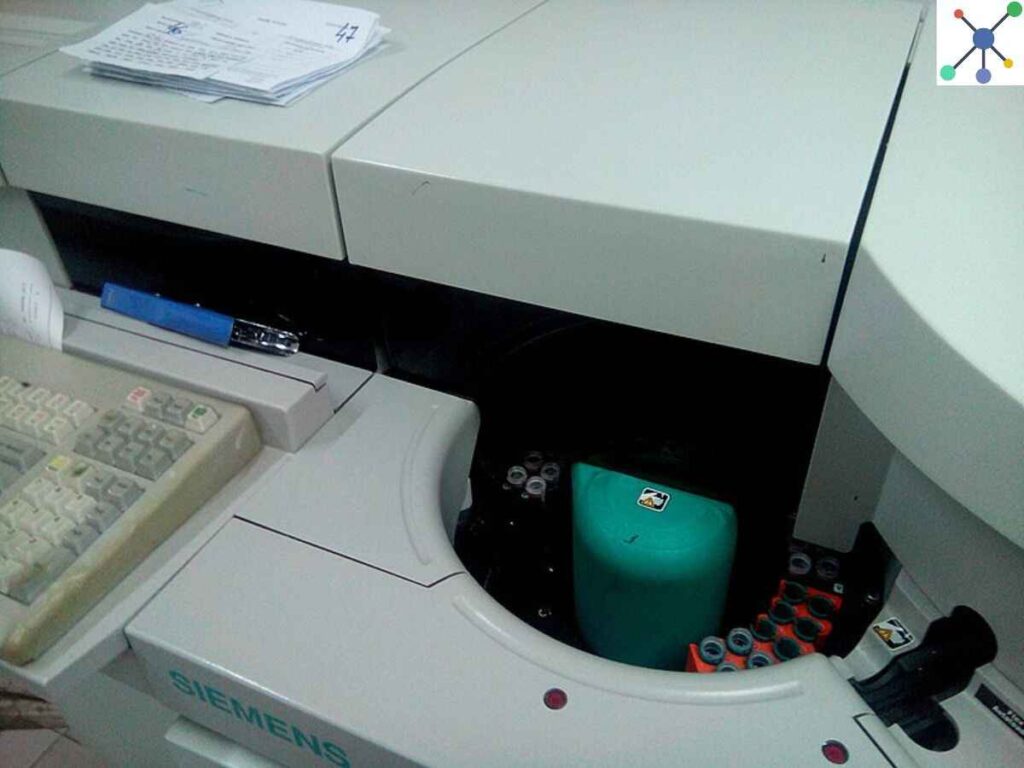

These instruments are very much helpful for the analysis of materials like glucose, enzymes, electrolytes, and lipids, which allows doctors to evaluate a variety of diseases, from various kidney disease to diabetes.
Basically, a biochemistry analyser is a tool that detects and measures the presence of particular molecules whixh are present in a sample by use of chemical processes.
The analyser adds reagents or chemicals that react with the components in the sample — when a blood or urine sample is inserted.
The device then measures for any change in colours, light emission, or electrical signal that can often be generated by this reaction to figure out the substance’s quantity.
Biochemistry analysers are available in many different kinds of forms, including completely computerised units that are essential in highly populated environments like hospitals since they can process hundreds of samples in a single day.
Minor, semi-automated machines are also in use in research labs and minor clinics. By lowering human error, the automation level contributes to more precise and trustworthy outcomes.
These analysers are essential for giving rapid and precise diagnostic data so that medical professionals may decide how best to treat their patients.
As for an example, checking glucose levels assists in controlling the symptoms of diabetes, and checking enzyme levels in human body can reveal data concerning the health of the liver.
With capabilities including real-time monitoring, data management, and interface to hospital information systems, biochemistry analysers have undergone improvements in recent years.
Producing quicker test results and more efficient operations are made possible by this integration, which is crucial in emergency situations.
Biochemistry Analyzer Uses and Applications
Common Applications of Biochemistry Analyzer in Medical Diagnostics
In the world of health care diagnosis, biochemistry analysers are essential instruments that are important to the identification, tracking, and treatment of a wide range of medical problems.
These devices are made to analyse bodily fluids, including blood, and they provide vital information that aids in the decision-making of medical professionals.

The treatment of diabetes is one of the most widespread uses for biochemistry analysers.
These gadgets enable physicians to monitor and regulate a patient’s blood sugar, guaranteeing that it stays within a safe range, by measuring the amount of glucose present in the blood.
This is essential for the diagnosis of diabetes as well as for the avoidance of consequences such as impaired kidney function, damage to neurones, and heart problems.
Biochemistry Analyzer Uses in Liver Function Test
Analysers for biochemistry are also frequently used to track renal and liver function. As for an example, they can detect liver health by measuring the levels of enzymes like AST (aspartate aminotransferase) and ALT (alanine aminotransferase).
Increased hepatic enzyme levels could indicate an illness or damage to the liver. In a similar vein, these analysers evaluate renal function by measuring blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine, which provide crucial information for the identification and treatment of kidney diseases.
Biochemistry Analyzer Uses in Lipid Profile Test
Lipid profile testing is a significant additional use. Triglyceride and cholesterol levels are measured using biochemistry analysers, which are essential for evaluating cardiovascular health.
Increased concentration of these lipids may signify a higher chance of heart disease, enabling immediate attention, care and therapy.
Biochemistry Analyzer Uses in Endocrine Function Test
Moreover, a variety of metabolic illnesses, electrolyte imbalances, and conditions pertaining to endocrine function, including thyroid disease, are diagnosed and tracked with the use of these analysers.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels, for example, can be measured, which is important for determining if a patient has hyper- or hypothyroidism.
In conclusion, biochemistry analysers play a critical role in medical diagnostics by providing precise and on time results that are necessary for the successful treatment of a variety of medical disorders.
Biochemistry Analyzer Uses in Clinical Laboratories
In clinical laboratories, biochemistry analyzers are essential tools for diagnosing, tracking, and treating a wide range of medical disorders.
These devices are made to examine body fluids, mainly blood and urine, and provide crucial data which helps doctors make decisions.
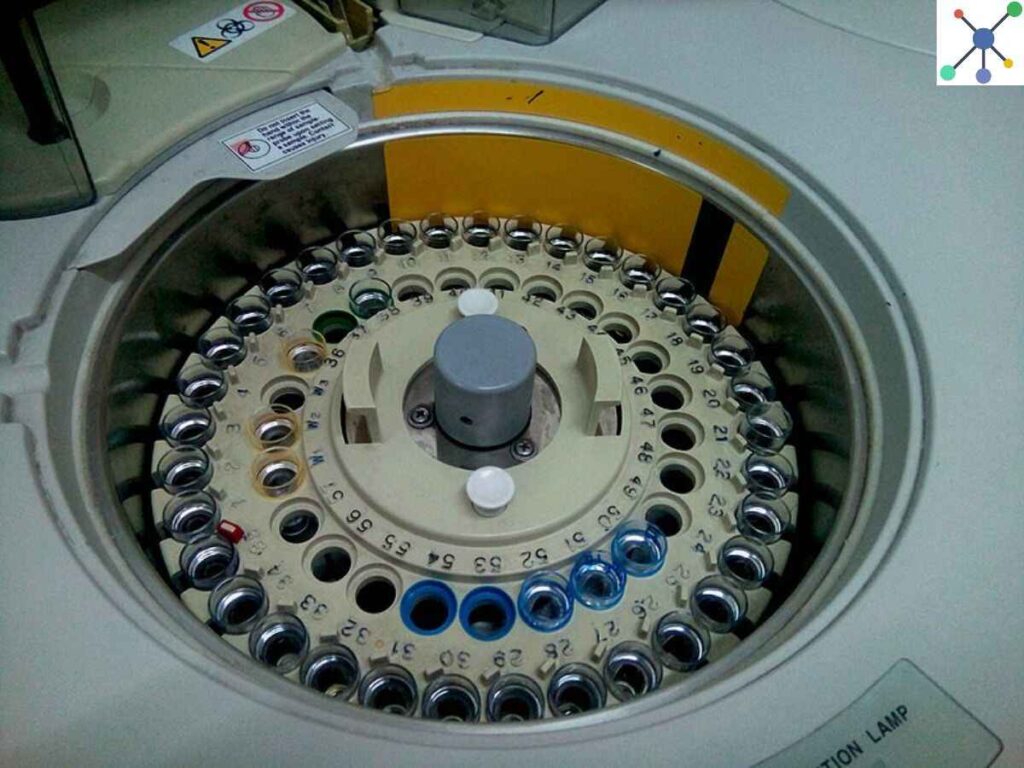
Periodic blood chemistry panels are one of the main uses of biochemistry analyzers in clinical laboratories.
These panels provide an in-depth understanding of a patient’s metabolic and organ function and often include tests for glucose, electrolytes, proteins, and enzymes.
For instance, electrolyte levels are essential for evaluating hydration, kidney function, and acid-base balance, while glucose readings are critical for identifying and treating diabetes.
Biochemistry analyzers are widely employed in the evaluation of liver and kidney function in addition to standard tests.
Biochemistry Analyzer Uses in Measuring Enzymes
These devices measure enzymes like aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT), which aid in the detection of liver illnesses like hepatic cirrhosis and hepatitis.
Analyzing blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine levels additionally brings light on kidneys health and can help diagnose diseases like chronic kidney disease.
Another popular use for biochemistry analyzers is lipid profile testing, which checks triglyceride and cholesterol levels.
In order to determine cardiovascular risk and allow early action to avoid heart disease, several tests are necessary.
It’s crucial to keep an eye on cholesterol levels in people who are at high risk of heart related problems or have a history of cardiovascular problems.
What is the Working Principle of Biochemistry Analyzer?
A biochemistry analyzer operates on a multi-step principle. Initially, a tiny sample of the patient’s blood or fluid is taken.
Step 1: Collecting The Sample
After that, the analyzer is filled with this sample. The device analyses the sample using electrical or optical signals.
As for an example, spectrometry is a technique used by some analyzers that measures the amount of light that is dispersed or absorbed by the sample by putting light on it. Different chemicals within the sample can be identified with the use of this method.
A biochemistry analyzer operates on a multi-step principle. Initially, a tiny sample of the patient’s blood or fluid is taken.
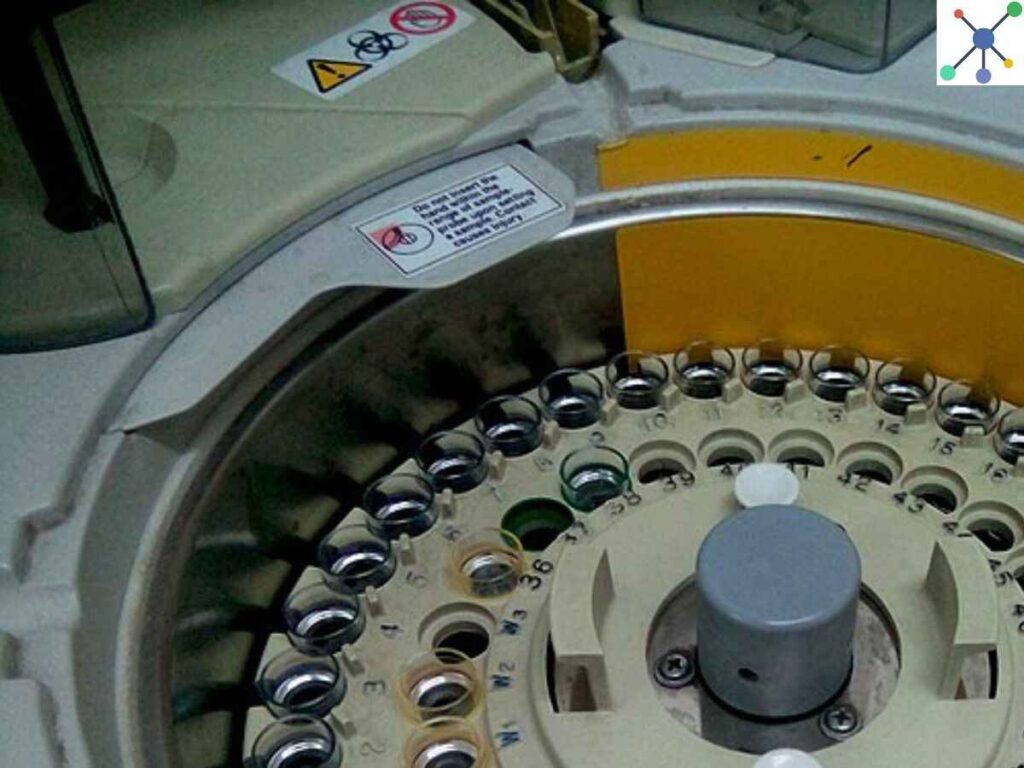

Step 2: Filling the Analyzer
After that, the analyzer is filled with this sample. The device analyses the sample using electrical or optical signals.
As for an example, spectrometry is a technique used by some analyzers that measures the amount of light that is dispersed or absorbed by the sample by putting light on it.
Different chemicals within the sample can be identified with the use of this method. Chemical reactions are applied by the analyzer to identify particular chemicals.
For instance, the analyzer mixes the sample with a reagent that reacts with glucose to produce a color shift while detecting glucose, a form of sugar. The glucose concentration may be further calculated by the machine by measuring the color’s intensity.
The levels of different substances are finally shown on a display. Physicians use this information to monitor patients’ health, identify illnesses, and decide on courses of therapy.
Biochemistry analyzers help doctors know patient’s health and make wise decisions by employing these modern techniques.
In conclusion, a biochemistry analyzer is a very useful instrument that, through the analysis of minute samples and measurement of vital substances, reveals the workings of the human body and plays an essential role to the preservation of health.
How Does Biochemistry Analyzer Work?
A biochemistry analyzer is a device that looks at your blood or other bodily fluids to help researchers and healthcare professionals understand what’s happening within your body.
Here’s how it functions in a way that can be understood.
First, a tiny sample of your blood is drawn by the physician or nursing professional. The biochemistry analyzer is thereafter filled with this blood sample. Many tiny instruments and computers work together inside the machine to search for particular substances, such as sugar, proteins, or lipids, in your blood.
The device makes use of “reagents,” which are certain chemicals that interact with the components present in our blood. A chemical reaction occurs when these reagents come into contact with your blood. The machine can measure the color change or light produced by the above procedure.
These color or light differences are detected by sensors in the biochemistry analyzer. The machine’s accuracy is far greater than our eyes’ ability to tell the differences between distinct colors. The data is subsequently sent by these sensors to an analyzer computer.
After that, the computer compiles all of the data and compares it to what is considered typical for a healthy individual. It examines the concentration of each component in your blood and determines if it is at the ideal level, too low, or just perfect.
The biochemistry analyzer then generates a report with the results it has found. The medical professional can then utilize this information to gain additional insight into your condition.
For instance, you may have diabetes if your blood sugar level is abnormally high. A biochemistry analyzer functions similarly to a detective by analyzing your blood to reveal evidence about your overall health.
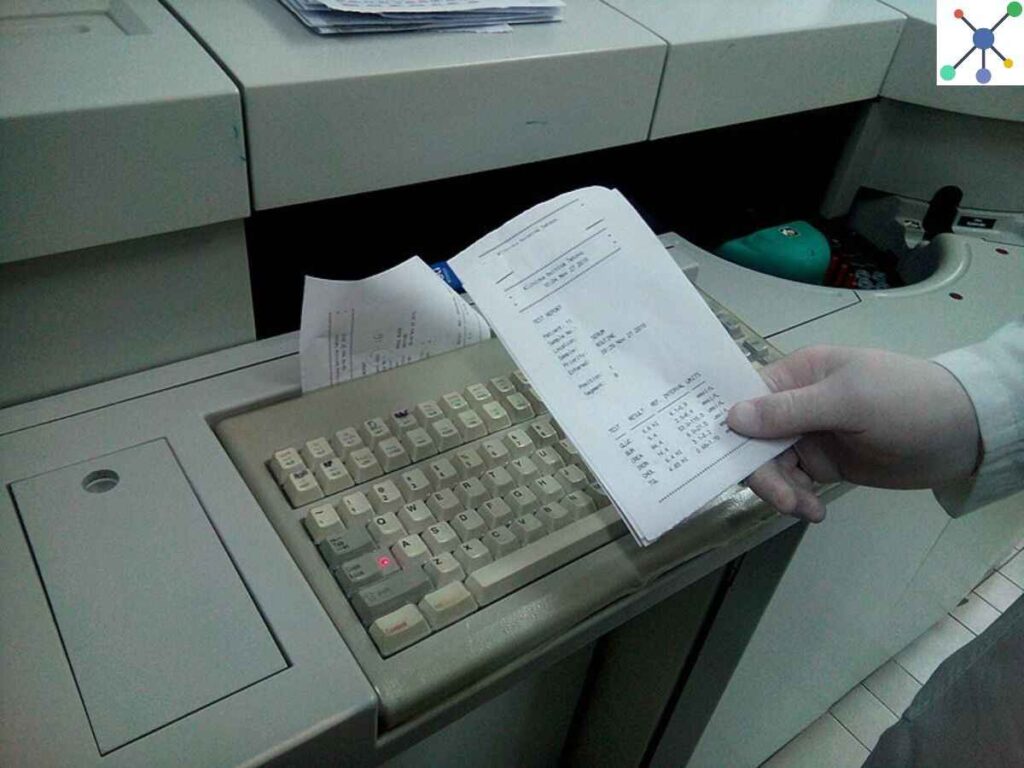

How Many Types of Analyzers Are There in Biochemistry?
Scientists evaluate various compounds in biological samples using a variety of analyzer types in biochemistry. These analyzers help in the identification of diseases and provide us with a better understanding of how our bodies function.
Clinical BioChemistry Analyzer
The clinical chemistry analyzer is one popular kind of analyzer. The clinical chemistry analyzer is useful to analyze different compounds found in blood and other liquids.
They can test for essential elements that reveal information about an individual’s health, such as proteins, glucose, and enzymes.
For instance, research has examined various clinical analyzers to figure out how well they measure biochemical compounds in animals like birds and turtles.
Microfluidic BioChemistry Analyzer
The microfluidic biochemistry analyzer is another type of chemical analyzer. These are more compact devices capable of testing very small volumes of liquid.
They can evaluate many samples at once and are extremely fast. In scenarios when larger equipment cannot be used, such as in the field, this is very helpful for rapid tests.
Point Care BioChemistry Analyzer
Point Care BioChemistry Analyzer are movable equipment that provide instant testing at the patient’s location. This implies that physicians won’t need to send samples to a lab in order to get results rapidly.
Spectroscopic BioChemistry Analyzer
The properties of substances are measured by spectroscopic chemistry analyzers using light. Based on how various compounds absorb and produce light, they can be used to classify them.
In conclusion, a variety of analyzers are used in biochemistry, each having a specific function in the study of biological processes and health.
These include spectroscopic biochemistry analyzers, clinical chemistry analyzers, microfluidic devices, and point-of-care biochemistry analyzers.
What Are The Parts Of Biochemistry Analyzer?
The various parts of Biochemistry Analyzer are:
- Sample Holder
- Pipette
- Reagent Section
- Mixing Area
- Incubator
- Detector
- Computer
Sample Holder
This is the place to put the sample of blood or urine.
Pipette
Pipette is a small straw like structure. It is used to transfer a little amount of sample to a particular section of the machine.
Reagent Section
Reagent Section is a section where the machine adds particular substances, or reagents, to the sample.
These compounds trigger changes in the sample that aid in the identification of various substances in our blood or urine.
Mixing Area
The sample must be stirred once the reagents have been added. The mixing section ensures that all ingredients are thoroughly mixed to promote uniform chemical reactions.
Incubator
In order to speed up the reactions, the collected material may need to be warmed up after the mixing process.
For a brief while, the sample is kept at the proper temperature by the incubator, which functions similarly to a miniature oven.
Detector
After the reagents are added and mixed, this section examines the sample to determine what changes have occurred in it. It measures the changes and collects essential details about the sample using light.
Computer
In the end a computer receives all of the detector’s data. After processing this data, the computer notifies the medical professional about the contents of the sample and whether it is normal or causes for worry.
What Is The Basic Function Of Biochemistry Analyser?
This device is mostly used for helping clinicians in determining whether our bodies are functioning normally or if there is a problem.
For instance, a doctor may use a biochemistry analyser to figure out the amounts of specific compounds in a patient’s blood if they are experiencing constant fatigue.
In the event that the equipment detects abnormally high or low blood sugar, the physician can make the necessary corrections.
Because they generate data efficiently, quickly and accurately, biochemistry analyzers are extremely important.
This implies that physicians will not have to perform more complicated testing in order to understand what is taking place within a patient’s body. The equipment can do multiple simultaneous tests, saving time and allowing quicker decision-making.
A biochemistry analyzer functions similarly to a body detective. It uses indicators found in our blood and other bodily fluids to determine our level of health and need for treatment.
Doctors are thus able to precisely choose the method of treatment that will help us feel better.
Which Biochemistry Analyser Is Best?
The best analyser should provide a large selection of tests that fits the requirements of your research facility. It’s crucial to select an equipment which fulfils your needs because some are specialised in testing particular category of testes.
You will need an analyser that can conduct numerous tests rapidly if your laboratory receives a lot of samples. Certain analysers are perfect for busy laboratories because they are made for high quantity operations.
The machine’s operation should be simple and its user interface should be easy to understand. This boosts productivity and lowers the possibility of mistakes.
Seek for analysers with an excellent track record for providing precise and reliable tests readings.
A machine with good after-sales support and low maintenance will be the best option to buy.
The budget is also a factor to consider. Although they cost more, certain high-end analysers provide extensive functionality. It’s critical that you maintain a balance between the things you require and your budget.
Abbott, Siemens, Beckman Coulter, Roche, and Siemens are a few of the market’s well-known brands. These companies have produced genuine biochemistry analysers for a very long time use.
Also Read:
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Handwritten Notes
Structure of Atom Class 11 PPT
50 Examples Of Balanced Chemical Equations With Answers
Positive Deviation From RAOULT’S LAW – Explaination – Solution
Challenges and Limitations of Biochemistry Analyzers Use
Biochemistry are very useful for analysing the chemical composition of different body fluids, however they have some difficulties and limitations just like everything else.
Biochemistry Analyzers: Common Uses and Key Challenges in Healthcare
Complexity to use
Operating biochemistry analyzers can be a very challenging task. Despite their stated simplicity, the settings and instructions may sometimes be difficult to understand.
The outcomes may not be accurate if the guidelines have not been followed exactly.
Maintenance Problems
These electronic devices require routine maintenance and cleaning for proper functioning and operation. Improper maintenance might lead to malfunctions or incorrect outcomes.
Costly
The require routine maintenance and cleaning cost is very expensive. Not all hospitals or clinics can afford the most recent or the most significant machines, which may impact the quality of care patients receive.
Biochemistry Analyzers: Limitations
Biochemistry Analyzers Are Not Always Correct
Despite their superior technology, these robots are not perfect all the time. On rare cases, a tiny error in the preparation of the sample or the setup of the machine can cause the results to be incorrect.
Not Capable of Doing All Tests
Not every biochemistry analyser is capable of doing all tests. Certain laboratories have limited capabilities, therefore in the unlikely scenario when a physician requires a different test, they may need to ship the sample to another testing facility or make use of an alternate device.
Slow Processing Time
When observations are needed quickly in an emergency, it might be problematic as tests take a lengthy time to finish. The machines operate quickly, even though, occasionally we have to wait longer than we’d like to wait.
Understanding the biochemistry analyzer uses helps us see how important these machines are in health care. These analyzers perform vital tests that help doctors diagnose and treat illnesses, making sure we stay healthy.
The biochemistry analyzer uses include checking blood sugar levels, cholesterol, and even detecting diseases early, which can save lives.
By knowing the biochemistry analyzer principle, we can appreciate the science behind these tests and how they work to give us accurate results.
Remember, the biochemistry analyzer uses are not just about machines; they’re about helping people live healthier, happier lives.
If the article is helpful to you, please share with your family and friends.
1 thought on “Biochemistry Analyzer Uses and Principle: A Comprehensive Guide”