Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer: Get solutions, Our collection of Class 10 Physical Science Question Answers for either exams preparation or revision is always solved.
Obtain elaborate answers to the questions asked on a daily basis and increase your knowledge of Physics & Chemistry. Ready to score top in exams,
If you want Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer guide? Ideal for students in need of robust and accurate study tools.
- Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer
- Top 50 Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer Samples
- Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer: Chapter-Wise Breakdown
- Chapter 1: Electricity
- Chapter 2: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 3: Sources of Energy
- Chapter 4: Light – Reflection and Refraction
- Chapter 5: The Human Eye and the Colourful World
- Chapter 6: Electric Motor and Generator
- Chapter 7: Current and Resistance
- Chapter 8: Refraction of Light
- Chapter 9: The Universe
- Chapter 10: Radioactivity
- Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer Key: Solved Previous Year Papers
- Top 20 Numerical Problems in Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer
- Tips and Tricks for Tackling Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer Effectively
- Key Formulas and Definitions for Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer
- Frequently Asked Questions in Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer: Expert Solutions
- Conclusion: Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer
Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer
So without wasting time lets read the physical science class 10 question answer guide. The ultimate guide to preparing for your exams (or improving on what you know) Physical science is a subject that includes concepts related to electricity, magnetism and chemical reactions in class 10.
These concepts are essential to good results in your course.
In this resource, you have 10th Physical Science Question Set providing Class X students the opportunity to practise & get good at it. Formulated according to the latest curriculum, changes and trends making you more prepared than ever.
Once you complete these Question Answer sets of Class 10 Physical Science, Both theoretical and numerical problems will be solved by yourself. It will not only motivated you to perform better but this motivation would drive your interest in the further recognition.
Well!, Start your journey in the Physic or Chemistry with our Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer book and step ahead to learn. And we are here to help guide you along your journey.
Top 50 Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer Samples
Appearing for the Class 10 Physical Science exam. The Question Bank contains 50 sample questions with answers on physics and chemistry concepts.
These questions, from Newton´s laws to chemical reactions will help you understand and secure your confidence for the exam. Happy studying students!
1. What is the SI unit of force?
Newton (N) is the SI unit of force.
2. State Newton’s First Law of Motion.
In physics, this behavior is a restatement of Newton’s first law which says that an object in motion will stay at the same speed and direction indefinitely unless acted on by some external force.
3. Define power. How is it calculated?
The rate at which work is done. Below is the formula to calculate it:
Power (P) = Time taken (t)/Work done (W) →→ Power = t/W
The watt (W) is the unit of power in the International System of Units, with one joule per second.
4. What is Ohm’s Law?
Ohm’s Law — it says that the current passing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points, as long as temperatures remains steady.
The formula is: V=I×R
where V is the voltage, I is the current, and R is the resistance.
5. What is the difference between a concave and convex lens?
A concave lens curves inward at the center and out toward the edges, so it tends to spread light rays apart. A convex lens has a thicker centre and tapered edges, which focuses the light rays to converge.
6. Explain the greenhouse effect.
The greenhouse effect is the retention of radiation from solar light by a planet’s atmosphere, due to gases such as carbon dioxide, water vapor. In a special system, warm process are kept on Earth which is also responsible for global warming if it boosted by human activities.
7. What is the law of conservation of energy?
The First Law of Thermodynamics (Conservation) states that energy is always conserved, it cannot be created or destroyed in an isolated system. Conservation of Energy: The total energy in a closed system is conserved.
8. State the formula for calculating kinetic energy.
The formula that describes kinetic energy is: K.E.= 1/2 mv2
where m is the mass of the object and v is its velocity.
9. What is electrolysis?
Electrolysis is the fewest possible process of using electricity to cause a chemical reaction. Or, it may be described as very simplest operation by which availability will use from charged ions in an electrolyte electrochemically reduced reactions at basic electrode and oxidation incuses are done on main even if elements.
10. What is the principle behind the hydraulic lift?
Pascal’s Principle states pressure applied to a confined fluid is transmitted undiminished in all directions throughout the fluid. The hydraulic lift runs on this principle.
11. Define refraction of light.
Refraction is the bending of light that happens at a noninherent angle as it moves from one medium to another with varying optical density.
12. What is the speed of light in a vacuum?
The speed of light in a vacuum is approx. 3×108 meters per second (m/s).
13. Explain Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule.
Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule is to determine the direction of force in an electric motor. As per this rule, if the thumb of your left hand shows upward direction then forefinger in perpendicular to it means magnetic field downward and middle finger is also normal (right) one will show the direction of current.
14. What is the difference between heat and temperature?
Heat is the amount of energy that moves from one system to another. On the other hand, and temperature represents an average kinetic energy per unit between two systems.
15. What is a chemical reaction?
Chemical Reaction: A chemical reaction is the transformation of one or more substances (reactants) into new ones, which may have different properties.
16. State the law of reflection of light.
The law of reflection states that angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection and the incident ray, reflected ray normal at a point all lie in same plane.
17. What are isotopes?
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with equal protons but different neutrons
18. Define electromagnetism.
Electromagnetism is the branch of physics that deals with electric currents and magnetic fields.
19. What is nuclear fission?
Nuclear fission is when the core of a heavy atom splits, releasing energy.
20. How is the pH scale used to measure acidity or alkalinity?
The pH, which stands for the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. A pH value of less than 7 is acidic, a little more than seven neutral and the higher again an alkaline.
21. What is the law of multiple proportions?
The law of multiple proportions: When two elements combine to form more than 1 compound, the masses of one element which combines with a fixed mass of the other euth creative in small whole number ratios.
22. What is a galvanometer used for?
Galvanometer – A device to detect and measure very small electric currents.
23. What is acceleration? How is it calculated?
Acceleration: Change in velocity of an object per unit time. As Nirra Wrigley explains, it can be calculated with this formula: a=Δv/t
where a is acceleration, Δv is the change in velocity, t is the time taken.
24. What are covalent bonds?
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of pair of electrons between atoms.
25. What is the refractive index of a medium?
The refractive index of a medium is defined as the ratio of speed by which light travels in vacuum to that in the medium.
It shows the extent by to which this light is slowed down and even partially bent as it would enter that medium.
26. Define displacement in terms of motion.
Conceptually, displacement is the shortest straight distance from your object’s starting point to its ending position (magnitude) with a direction. It is a vector quantity.
27. What are conductors and insulators?
Conductors: Materials which have the ability to permit electricity charges freely move through them. e.g., Metals Insulators are materials which do not conduct electricity, i.e., they resist the flow of electric charges (e.g. Rubber or plastic)
28. What is a periodic table?
A periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, ordered by atomic number and organized according to their physical properties.
29. What is a mole in chemistry?
A mole is a unit on the amount of substance. By definition, it has Avogadro’s number of atoms or molecules in a sample.
It is defined as containing exactly 6.022×1023 atoms or molecules.
30. What is the formula for work done?
The formula for work done is:
W=F×d
where W is work, F is force and d the displacement along that force.
31. What is a displacement reaction?
A displacement reaction is a chemical reaction in which a more reactive element displaces from its compound to combine with another less reactive element.
32. Define amplitude in the context of waves.
Amplitude: The amplitude of a wave is the maximum displacement of any point on it from its equilibrium position. It is what gives the wave energy and power.
33. What is thermal conductivity?
Thermal Conductivity — It is the ability of a material to conduct heat. Materials with high thermal conductivity convey heat better than materials of lower conductivity.
34. Explain what happens during chemical equilibrium.
At chemical equilibrium, the rate of forward reaction is equal to that for reverse process and concentrations of reactants as well as products are constant.
35. What is the relationship between mass and weight?
Mass is the measure of a quantity of matter and it does not change depending on location. Weight is the force exerted by gravity on an object, which can be determined via:
This is the weight, actually; Weight=Mass×Gravity
In other words, weight varies with the strength of a gravitational field.
36. What is an electromagnet?
Electromagnets is a type of magnet that created by passing electricity through a coil of wire, ending up with an magnetic field.
37. Explain the pH value of a neutral solution.
A neutral solution (such as pure water), has a pH of 7 and half molarity each on hydrogen ions and hydroxide ion; if the hydrogen contributes is harder than hydroxide it forms acid.
38. What is the formula for calculating the density of a substance?
The formula for density is:
The density of a substance is given by Density=Mass/Volume.
Density is measured in kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³), the SI unit.
39. Define wavelength in the context of light waves.
The distance between two identical points in a wave is called the wavelength (e.g. from peak to peak, or trough to trough).
40. What is the Doppler effect?
Doppler effect is the change in frequency or wavelength of a wave when a source observer on rest conditions changes to motion and vice versa. Commonly seen for sound waves when an object moves towards or away from the observer.
41. What is the difference between series and parallel circuits?
Components are connected end to every in a series circuit; only one current can flow through them,
In a parallel circuit, all components/receivers are connected between the same two points or nodes, so phase difference of voltage across each element is zero but current through them may be different.
42. Explain the law of universal gravitation.
The law is called the Law of Universal Gravitation because it states that every particle in the universe attracts all other particles.
43. What is an alloy?
An alloy is a blend of two or more elements, including at least one metal. Alloys have superior qualities, for example strength or corrosion resistance.
44. What is an exothermic reaction?
Exothermic reaction: A chemical reaction which releases heat energy is called exo-thermic reaction as a result the surroundings will become hot.
45. Explain Boyle’s Law.
If the temperature can remain constant and we do not add or remove gas to what was initially being measured, Boyle’s Law(proposed by Robert Boyle in the 17th century) deals with this exact concept of pressure increased decaying as volume is expanded. Mathematically:
P×V=constant
Now, for the ideal gas law, P = Pressure and V = Volume.
46. What is an electrolyte?
An electrolyte is a substance which, when dissolved in water, conducts electricity due to the presence of ions.
47. Define momentum.
The product of the mass and velocity of an object is called momentum. It is a vector quantity and computes with the formula:
Momentum=Mass×Velocity
48. What is Archimedes’ Principle?
This property can be defined in terms of Archimedes’ Principle which states that any object, wholly or partially immersed in a fluid, is buoyed up by a force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by its volume.
49. What is nuclear fusion?
What is nuclear fusion — A process in which two light atomic nuclei combine and form a heavier nucleus, releasing enormous energy. It is this process that fuels the Sun and all other stars.
50. State the formula for calculating pressure.
The formula for pressure is:
P=F/A
If P is pressure and F, the force. A is the area over which the force is applied, then; Pressure is Pascal (SI unit: pascal, Pa).
Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer: Chapter-Wise Breakdown
In Simple Language, Today I am sharing that “Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer: Chapter Wise”. Well, this guide will walk through every important concepts and questions to be asked in each chapter.
We give you all the answers that you have been looking for, while preparing exams or just going through your major points.
This will help you learn with confidence as it offers clear explanation and solved examples. After practicing these Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer in order to prepare for the exams. Meaning go through each chapter and learn the concepts well
Chapter 1: Electricity

Q1. What is the SI unit of electric current?
Ampere (unit of electric current in international system unit) [I]
Q2. Define electric power.
Electric power is electrical energy consumed in a specific rate by the circuit. It is measured in watts (W).
Q3. State Ohm’s law.
According to Ohm’s law — the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to voltage across it provided temperature remains constant. Mathematically, V = IR.
Q4. What is the relationship between power, voltage, and current?
Power: The power (P) = Voltage(Volt -V), Current(Ampere-I): P=VI.
Q5. How does resistance affect the flow of current in a circuit?
Resistor resists current (current phase shift). Resistance can also be measured as how much it resists the flow of current and so its value is directly proportional to lower armature currents.
Chapter 2: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Q6. What is a solenoid?
A solenoid is a circular coil of wire that creates an electrical current through it to additionally induce in this way magnetic area.
Q7. What is the function of a galvanometer?
A galvanometer is an electromechanical transducer that converts a small electric current to deflection of a mechanical circular coil.
Q8. State Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule.
Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule says thatSimply, The thumb shows the direction of motion (force), fore-finger showing magnetic field and middle finger is for flow current.
Q9. How can the strength of an electromagnet be increased?
You can increase the power of an electromagnet by increasing the current or number of coils, and also by using a soft iron core.
Q10. What happens when a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field?
The conductor experiences a force, causing it to move if the current and magnetic field are perpendicular.
Chapter 3: Sources of Energy
Q11. What is renewable energy?
As the name suggests, renewable energy comes from natural resources that are replaced by nature over time—sunlight, wind and hydropower among others.
Q12. Define fossil fuels.
Fossil fuels Fossil fuels are non-renewable, since they were formed from the remains of ancient plants and animals. like coal, oil and natural gas.
Q13. What is nuclear energy?
Nuclear energy is the released form of nuclear reactions, particularly fission and fusion.
Q14. What are the disadvantages of using fossil fuels?
They pollute the air, accelerate climate change but most importantly they are finite and will someday run out.
Q15. Why is solar energy considered the best renewable energy source?
One of the most sustainable energy sources is Solar Energy, as it comes in abundant forms without any pollution and inexhaustible.
Chapter 4: Light – Reflection and Refraction

Q16. What is the law of reflection?
Law of reflection, states that Incident angle is equal to angel of Reflection.
Q17. Define refraction of light.
So, what is refraction after all? Refraction happens when light strikes a surface that changes the speed of it.
Q18. What is the refractive index?
The ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to that in any other medium is called index refraction.
Q19. How does a convex lens affect light rays?
The light rays are converged into a focal point by converging lenses which formed object image.
Q20. What is the nature of the image formed by a concave mirror when an object is placed at the focus?
An object kept at the focus of a concave mirror, would give rise to highly magnified true inverted image.
Chapter 5: The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Q21. What is the function of the retina in the human eye?
The retina is the layer of cells at back part of he eye, getting light and turning it into electrical messages sent to the brain.
Q22. What is the least distance of distinct vision for a normal eye?
The limit of distance of minimum clear vision for a normal eye is 25 cm.
Q23. What is myopia, and how can it be corrected?
Short-sightedness (myopia) — where distant objects appear blurry But a concave lens can correct it.
Q24. What is the dispersion of light?
When white light is made to pass through a prism, the spectrum of sunlight can be formed due to scattering which occurs when each wavelength has its angle and degree of separation.
Q25. Why does the sky appear blue?
Blue light is scattered in all directions by the tiny molecules of air in Earth’s atmosphere; you see blue wherever your line of sight from the surface passes through a large volume of air.
Chapter 6: Electric Motor and Generator
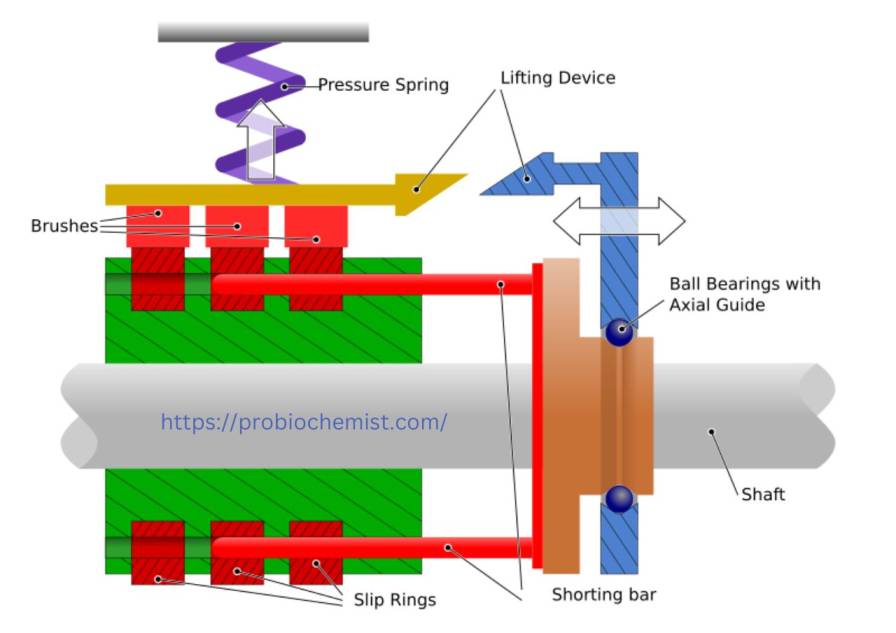
Q26. What is the principle of an electric motor?
Electric motor is based upon the principle, in a magnetic field, force experience by current-carrying conductor.
Q27. What is electromagnetic induction?
Electromagnetic induction: Producing a current in a conductor by changing the magnetic field around it.
Q28. What is the difference between a generator and a motor?
A motor changes electrical energy into mechanical, — a generator goes the opposite way an generates electiricty formmechnical motion.
Q29. What are the main components of a DC motor?
A DC motor has more parts than an AC Motor… Armature, Commutator…..Brushes……Field Magnets…the basics….
Q30. What is the function of a commutator in a motor?
A commutator causes the current in the armature to reverse, thus allowing the motor again rotate in one direction.
Chapter 7: Current and Resistance
Q31. What is resistivity?
Resistivity (ρ) is a material’s ability to resist the flow of electric current, measured in ohm-meters.
Q32. How does the resistance of a conductor depend on its length and area?
The resistance increases as the length of a conductor and decreases with its cross-sectional area.
Q33. What are superconductors?
Superconductors are materials that show zero resistance at very high low temperatures.
Q34. What is the role of a fuse in an electric circuit?
A fuse is a safety device that works to safeguard electrical circuits by breaking and melting the circuit as soon overcurrent flows through it.
Q35. What is the advantage of connecting resistors in parallel?
Parallel resistors are reducing the total resistance and provide several ways to pass over current.
Chapter 8: Refraction of Light

Q36. Why does light bend when it passes from one medium to another?
Bring it down light refracts as it goes from one medium to another, that has a different index.
Q37. What is total internal reflection?
A phenomenon in which the light is reflected at the boundary of a denser medium instead of being refracted, this process we call it Total internal reflection.
Q38. What are the conditions for total internal reflection?
TIR occurs when light is moving from a denser medium to a rarer one and the angle of reflection exceeds critical angle.
Q39. What is the critical angle?
The critical angle is the incident angle at which light is refracted along with boundary and totally reflect.
Q40. How do optical fibers work?
The use of optical signals and total internal reflection allow light to travel large distances through a material with little loss is in the so called Optical fibers.
Chapter 9: The Universe
Q41. What is a galaxy?
A galaxy is basically a large ensemble of stars, planets, gas and dust that binds itself by gravity.
Q42. What is the Big Bang Theory?
The Big Bang Theory explains how the universe began as a very hot, small and dense superforce approximately 13.8 billion years ago (nearly scientific time) and has been expanding ever since.
Q43. What is a black hole?
A black hole is an area in outer space with a very strong gravitational force, so that nothing inside it can ever escape.
Q44. What are constellations?
Constellations are groups of stars that create pleasing shapes in the sky.
Q45. What is the Milky Way?
Our solar system is located in the Milky Way, which itself is a spiral galaxy.
Chapter 10: Radioactivity
Q46. What is radioactivity?
In physics, radioactivity (also radioactive decay or nuclear decay) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy (in terms of mass in its rest frame) by emitting radiation, such as an alpha particle.
Q47. What are alpha particles?
Alpha particles are made of two protons and two neutrons and have a positive charge.
Q48. What is half-life in radioactivity?
Half life is the time it takes for half of a sample particles to decay.
Q49. What are gamma rays?
Gamma rays are frequents emitted as part of the radioactive decay.
Q50. How is nuclear fission different from nuclear fusion?
Nuclear fission refers to a heavy nucleus breaking down into smaller nuclei while nuclear fusion entails the coming together of light nuclei.
These may also help you:
Class 12 Physics Handwritten Notes | [Chapterwise] | PDF
Plus One Zoology Chapter Wise Questions and Answers – PDF
Plus One Botany Notes – PDF Download Chapter Wise Q&A
Human Reproduction Class 12 PPT – PDF – Plus 2
Chemistry Laboratory Apparatus and their Uses with Pictures pdf
Variation of Conductivity and Molar Conductivity with Concentration
Poisson’s Ratio in Thermodynamics – Derivation
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Handwritten Notes | Class 12 | Pdf
Structure of Atom Class 11 PPT – Class 10, Class 9
50 Examples Of Balanced Chemical Equations With Answers PDF
Positive Deviation From RAOULT’S LAW – Explaination – Solution
Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer Key: Solved Previous Year Papers
Studying for exams can be tough, but having the right tools or resources can help you overcome those challenges and really make a difference.
Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer Key — This Class 10 Physical Science (PS) Question answer key consists of a selection of Solved Previous Year Questions to enhance practice and grip over some concept points.
By learning these questions and answers, students can develop problem-solving capabilities and increase the confidence in exams. This Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer guide is perfect for revisiting what you´ve learned or to test your knowledge.
This resource here helps you access some of the critical Question Answer samples from Class 10 Physical Science and improve in your studies.
Top 20 Numerical Problems in Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer
Class 10 Physical Science is the study of such principles which helps students learn about nature and apply what they have learned.
Numerical problems have a great importance in that they help to apply the concepts which we read, used to solve such types of numericals. This article consists of 20 Numericals based on the class 10 physical science and are most important, interesting topics.
1. Problem: Calculate the force required to accelerate a 10 kg object at 2 m/s².
Answer: F=ma; F=10×2=20 N The required force is 20 N.
2. Problem: A car travels 150 km in 3 hours. What is its average speed?
Answer: 𝑣 = 𝑑/𝑡 = 150/3 = 50 km/h. The car’s average speed is 50 km/h.
3. Problem: Find the work done when a force of 5 N moves an object by 3 meters.
Answer: W=F×d=5×3=15 J; The work done is 15 joules.
4. Problem: Calculate the kinetic energy of a 2 kg object moving at 4 m/s.
Answer: KE=1/2 mv2 = 1/2 ×2×(4)2 =16 J; The kinetic energy is 16 J.
5. Problem: What is the potential energy of a 5 kg object at a height of 10 m (g = 9.8 m/s²)?
Answer: PE=mgh=5×9.8×10=490 J; The potential energy is 490 J.
6. Problem: Find the power of a machine that does 200 J of work in 5 seconds.
Answer: P=W/t =200/5 =40 W; The power is 40 watts
7. Problem: A resistor has a resistance of 5 ohms, and a current of 2 A flows through it. Calculate the voltage.
Answer: V=IR=2×5=10 V; The voltage is 10 volts.
8. Problem: Find the time taken for a car moving at 20 m/s to stop if the deceleration is 4 m/s².
Answer: t= v/a =20/4 =5 s; The time taken is 5 seconds.
9. Problem: If a 6 V battery is connected to a 3-ohm resistor, what is the current flowing through it?
Answer: I=V/R =6/3 =2 A; The current is 2 A.
10. Problem: A light bulb uses 100 J of energy in 10 seconds. What is its power?
Answer: P=W/t =100/10 =10 W; The power is 10 watts.
11. Problem: A force of 50 N is applied at an angle of 60°. Find the horizontal component of the force.
Answer: Fx =Fcosθ = 50cos60∘= 50×0.5=25 N; The horizontal component is 25 N.
12. Problem: A body has a mass of 8 kg. What is its weight on Earth (g = 9.8 m/s²)?
Answer: W = mg = 8×9.8 = 78.4 N; The weight is 78.4 N.
13. Problem: Calculate the charge when a current of 3 A flows for 5 seconds.
Answer: Solution: 𝑄 = 𝐼 x 𝑡 = 3 × 5 = 15 C; The charge is 15 coulombs
14. Problem: A car moving with a speed of 30 m/s comes to a stop in 10 seconds. What is its deceleration?
Answer: a = v/t = 30/10 =3 m/s2; The deceleration is 3 m/s²
15. Problem: What is the wavelength of a wave with a frequency of 10 Hz and a speed of 340 m/s?
Answer: λ= v/f = 340/10 = 34 m; The wavelength is 34 meters.
16. Problem: If 500 J of work is done in moving an object 10 meters, find the force applied.
Answer: F= W/d = 500/10 =50 N; The force is 50 N.
17. Problem: Calculate the momentum of a 5 kg object moving at 6 m/s.
Answer: p = mv = 5×6 = 30 kg m/s; The momentum is 30 kg m/s
18. Problem: A force of 100 N moves an object by 20 m in 4 seconds. What is the power?
Answer: P=F×d/t =100×20/4 =500 W; The power is 500 watts.
19. Problem: Find the potential difference if 5 C of charge does 10 J of work.
Answer: 𝑉=𝑊/𝑄=10/5=2V; The potential difference is 2 V.
20. Problem: Calculate the gravitational force between two 1 kg masses 1 meter apart (G = 6.67 × 10⁻¹¹ N·m²/kg²).
Answer: F = Gm1. m2 /r2 = 6.67×10−11×1×1 / 12 = 6.67×10−11 N; The gravitational force is 6.67 × 10−11 N.
Tips and Tricks for Tackling Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer Effectively
Class 10 Physical Science questions may seem tough to tackle, but with the right methods and practice one can easily fare well.
Here are some prompts to get you thinking (and a downloadable worksheet for all of them on the bottom).
1. Know the Syllabus and Exam Pattern
The very first thing to master Class 10 Physical Science is to know the syllabus and exam pattern. Identify the chapters that are particularly significant for example Light, Electricity, Chemical Reactions.
That is where knowing the pattern of your exam will help you in preparing a study strategy. Like: how many marks for theory, numerical questions or diagrams etc.
2. Clear Your Basics for Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer
Concepts are used a lot in science, so make sure you know the basics. Focus on important topics like laws of reflection and refraction, Ohm’s law, chemical equation periodic classification in this chapter.
If you are struggling with any of the concept then go back once again to your books or asked your teacher for an extra revision. When your basics are clear, it may be easier for you to answer question from those concepts.
3. Solve The Numericals and Draw Diagrams for Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer
Exercises On Numericals, which is not exclusive of Physics. Solve Questions based on Electricity, Force and Optics. Write out the equation first, plug in what you know about (don’t forget your units), and tackle.
Also, diagrammatic representations of human eye, ray diagrams and electric circuits should be practiced. Neatly labeled diagrams tend to bring additional marks.
4. Use Keywords in Theory Answers
For theory based questions, language should be proper scientific. Example: If the question is related to electrolysis, use words like anode, cathode and electrolyte in your answer so that even if it needs some marking,then also teachers could at least get marks.
5. Time Management in Exam
Physical Science papers tend to be really long so knowing how to manage time is as important. And then start with the easiest to answer questions that you know for state marks.
Use this time to practice one section, and make room for self revising at the end.
6. Solving Last 4–5 Years Question Papers & Sample Papers.
Question papers and sample papers of previous year are the goldmine to know about exam pattern as well important questions. Even when you solve those, it gives you a sense of the probable question that could be asked and can rehearse them more or less within time limits.
If you follow these tips and practice regularly, then can take Class 10 Physical Science question answers more confidently and score high marks in exam.
Key Formulas and Definitions for Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer
This One Information provides the top 15 important formulas and definitional related to Physical Science for all those students who are currently studying in Class 10. The following can greatly help in increasing the speed of solving exam questions.
- Speed = Distance / Time. This formula is used to determine the speed at which an object moves. It’s important in kinematics.
- F=ma where,m = Mass, a = Acceleration. That is Newton’s second law of motion, saying when a force acts upon an object how does the movement of this object change.
- Suppose → Work = Force × Distance, W = F x D. It measures the work under a force acting on an object when displacement has taken place.
- Power = Work / Time (P = W/t). Power — how fast work is done
- This equation also tells us that the Kinetic Energy, KE = ½ × Mass × Velocity². The kinetic energy is a function of mass and velocity.
- P.E = m × g × h, Where P. E is the Potential Energy of a body & It’s given by mass. So it defines the weight or related to weights multiplied with height(h) and gravity (g), all together being exerted on that object! Potential Energy: It is the energy stored in an object because of its height.
- Ohm’s Law: V = IR. Voltage (V) = Current(I)* Resistance( R) in an electrical circuit.
- Electric Power = Voltage × Current (P= VI). The power in an electrical circuitTrail rather than start with this formula
- Refractive Index = Speed of Light in Vacuum / Speed of Light in Medium. In other words, it is the extent to which light deviates while moving from one medium into another.
- n₁sinθ₁ = n₂sinθ₂ (Snell’s Law). It describe the relation between angles and refractive indices while refraction.
- Density = Mass / Volume. The density shows us how tightly packed together a material is.
- Pressure = Force / Area. Pressure: Pressure is proportional to the force per unite area delivered.
- Acceleratinon = (Finnal Velocity – Iniital velocity)/Time. It demonstrates the rate of change in an object [speed].
- In order to calculate the momentum, use M = m v (whereas p is equal to mv). For each, granted the quantity of motion an object possesses is upcoming momentum.
- The gravitational force should follow an inverse square relationship: F = G (m₁m₂ / r²). It is used to calculate the gravitational influence of one mass on another.
Well, knowing the formulas and definitions will let you solve more complicated problems in physics exams.
Frequently Asked Questions in Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer: Expert Solutions
Physical Science of Class 10 sometimes creates many doubts among the students. This FAQ contains the most frequently asked questions related to motion, electricity magnetism and energy. These short answers make easy to grasp hard concepts and tough topics for students so that they can prepare well in their exams.
1. What is the Law of Reflection?
Answer: In easy term, the Law of Reflection states that
Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection
All these rays lie in the same plane which is called a Plane of incidence.
2. Define refraction of light.
Answer: Refraction is a phenomenon of bending the light when it travels from one medium to another in which speed changes. When speed of light is increased, it change its direction. E.g.,: when light enters water, it decreases its speed and bends towards the normal.
3. What is an electric circuit?
Answer: Electric circuit — A closed path which the electrons can flow through. A typical electric circuit may include a battery (power source), conductors i.e., copper wires, and/or any load such as resistance e.g. closing light bulb that utilizes the electricity to convert Photo voltaic effect into electrical energy by denoting Symbolism of Electricity.
4. Explain Ohm’s Law.
Answer: OHM-LAWS follow that current flows through a conductor between its two points is directly proportional to the voltage across these points if temperature remains unchanged This can be expressed mathematically.
V=IR
Where:
- V is the voltage,
- I is the current, and
- R is the resistance.
5. What is the difference between series and parallel circuits?
Answer: Components in series are all connected alongside one string, and every element extends the specific same present. After IF some gets down so total will be broken.
Within a parallel circuit, every component is connected across the same voltage source. Each of the components gets equal voltage, and if one fails to function all others keep working.
6. What is dispersion of light?
Answer: Dispersion refers to the splitting of white light into its constituent colors as it passes through a prism. This happens as different colored light bends differently by length.
7. Define work and give its formula.
Answer: Work is accomplished when force is applied to an object, resulting in a movement of the object in relation with its direction. The formula for work is:
W=F×d
- W is the work done,
- F is the force applied, and
- d is the displacement of the object.
8. What is the unit of power?
Answer: Power is measured in watts (W). Power: rate at which work is done or energy moved. Watt : The watt (symbol: W) is a unit of power, which can be defined in many ways; but always used to describe 1a Watt equals 1 Joule per second.
9. What is meant by magnetic field?
Answer: In physics, a magnetic field is a force that draws magnetized objects away and stops them from being pulled back. These magnetic field lines illustrate the strength of a given force and its direction.
10. What is a chemical reaction?
Answer: A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. It includes breaking and bonding the bonds of atoms.
These concepts FAQs are beneficial for class 10 physical science. A complete understanding of these topics will be very useful for your exams and in preparing a strong basis of Physics & Chemistry.
Conclusion: Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer
We wish this article of Class 10 Physical Science Question Answer is useful to you while learning and preparing for your exams.
Make sure to practice these ones as well with their answers so that you can take on your exams like a walk in the park. Consistency is key, after all.
If you like this guide, follow and share with friends or coworkers that may get value from it too. You guys will be able to lean on each other and change lives together.
We know you have questions and we are going to do our best to give all of you as much valuable information that will help steer us through these difficult times, so keep an eye out for new materials in the near future. Wishing you all the luck with your studies.