This Article is a Well Researched Article on Explaination and Solution on Positive Deviation From RAOULT’S LAW Derivation with Diagrams, Graphs and Examples.
Which Gives Positive Deviation from Raoult’s Law?
When the intermolecular forces between the various components of a solution are weaker than the intermolecular forces in the pure components, the solution exhibits a positive deviation from Raoult’s Law.
A mixture of acetone and ethanol Gives Positive Deviation from Raoult’s law.

Positive Deviation From RAOULT’S LAW – A to Z Details – Example, Diagram, Graph
What is Raoult’s Law?
Raoult’s Law is a chemistry principle that defines how the vapor pressure of a solution compares to the vapor pressures of its separate components present in it.
According to Raoult’s law, a solvent’s partial vapour pressure in a solution as well as in a mixture of multiple is equal to the vapour pressure of the pure solvent multiplied by its mole fraction in the solution.
The law has been named after a French Chemist, Francois Marie Raoult.
During his experiment, he discovered that when compounds were put into a solution, the solution’s vapour pressure reduced at the same time.
- Which Gives Positive Deviation from Raoult’s Law?
- What is Raoult’s Law?
- Is Delta V (ΔV) Positive in Positive Deviation?
- What is Positive Deviation from Raoult’s Law Azeotrope?
- Do Water and HCl Show Positive Deviation?
- What is Raoult’s Law of HCl : Aqueous Solution of Hydrochloric Acid?
- What is an Example of Raoult’s Law?
- What is Positive Deviation from Raoult’s Law Activity Coefficient?
- What shows Negative Deviation from Raoult’s Law?
- What is Positive and Negative Deviation of Raoult’s Law?
- What is the difference between Positive and Negative Deviation Class 12?
- What is an Example of Positive Deviation and Negative Deviation?
- Why HCl and H2O Show Negative Deviation?
- What is the Raoult’s Law Class 12?
- What is Positive and Negative Deviation from Ideal Gas?
- What is Negative Deviation from Raoult’s Law Entropy?
- What is Positive Deviation from Raoult’s Law Equation?
- What is an Example of Positively Deviated Solution?
- What is Mean By Positive Deviation?
- Which Liquid Shows Positive Deviation from Raoult’s Law?
- What is an Example of Non Ideal Solution Showing Positive Deviation from Raoult’s Law?
- What Type of Azeotrope is Formed by Positive Deviation from Raoult’s Law?
- What is an Example of Positively Charged Solution?
- Is Ethanol and Water Positive Deviation?
- What is Positive Deviation from Raoult’s Law Boiling Point?
- Positive deviation from Raoult’s Law Graph
Raoult’s Law States That:
- Each volatile component’s partial vapor pressure in a solution is calculated by multiplying the percentage of moles in the solution by the pure component’s vapor pressure.
- The total vapor pressure of a solution containing several volatile components is equivalent to the combined value of the partial vapor pressures of those components.
Is Delta V (ΔV) Positive in Positive Deviation?
The answer is ‘YES‘.
Positive Deviation from Raoult’s Law indicates a positive change in vapour pressure (ΔV).
This happens when the solution’s vapor pressure is higher than predicted by Raoult’s Law.
This happens usually because the interactions between the molecules in the solution are weaker than those in the pure substances.
When the volume rises and delta V becomes positive, the system is expanding and altering its surroundings.
However, as volume drops, delta V becomes negative and the environment works to compress the system.

What is Positive Deviation from Raoult’s Law Azeotrope?
A Positive Deviation Azeotrope is an example of azeotrope which takes place when Raoult’s Principle is deviated positively.
In this case, the azeotrope is defined as:
Increased Vapor Pressure
The total vapor pressure of the solution exceeds that anticipated by Raoult’s Law.
This occurs because the vapor pressure of the solution gets higher than that of the pure components due to the small number of intermolecular interactions in the solution.
Uniform Boiling Point
At any particular composition, the solution boils at an even temperature that is typically below the boiling points of the pure components but exceeds the boiling point predicted by Raoult’s Law.
This is known as an azeotropic composition.
In general, a positive deviation azeotrope is a combination in which the vapour pressure surpasses what Raoult’s Law suggests and the boiling point remains unchanged at whatever the proportion is.
Do Water and HCl Show Positive Deviation?
The escaping tendency from the solution to the vapour phase will be smaller if there is a stronger attraction between different molecules.
For instance, between the molecules of hydrochloric acid, also known as HCl, and the water (H2O).
As a result, the partial vapour pressure will be lower than Raoult’s law suggests, and the system is going to have a negative deviation.
What is Raoult’s Law of HCl : Aqueous Solution of Hydrochloric Acid?
Hydrochloric acid, also referred to as HCl in a solution behaves similarly to other solutions when Raoult’s Law is applied.
However because of its intense acidity and interactions with water, HCl and its solutions can exhibit certain unique behaviours.
PHCl = X.HCl . P0HCl
At which,
The partial vapour pressure of HCl over the solution is represented by PHCl .
The mole fraction of HCl in the solution is represented by XHCl.
And the vapour pressure of pure HCl in water is represented by P0HCl.
ALSO READ:
A to Z Body Parts Name | Human Body Parts that Starts With Different English Alphabets
How To Make Human Digestive System Model – 3D Model Project
Explain The Process Of Digestion In Human Beings

What is an Example of Raoult’s Law?
A mixture of Ethanol and Water can be the perfect example of Raoult’s Law.
Let’s say, we are dealing with a solution where the mole fraction of water is 0.3 and the mole fraction of ethanol is 0.2.
The vapour pressure generated by pure ethanol is equal 44 mmHg. And, pure water has a vapour pressure of 23 mmHg.
The partial pressure of ethanol and water can be calculated as:
(Knowing that, Partial Pressures = Mole Fraction x Vapor Pressure)
Partial Pressure of Ethanol = 0.2 x 44 = 8.8
Partial Pressure of Water = 0.3 x 23 = 6.9
Hence, Total vapor pressure of the solution = 8.8 + 6.9 = 15.7
Hence, Raoult’s Law explains how the presence of ethanol in water impacts the total vapour pressure above the solution in this case.
What is Positive Deviation from Raoult’s Law Activity Coefficient?
A solution that deviates positively from Raoult’s Law has an activity coefficient larger than one.
This shows that the solution is more active or deviates from the ideal behaviour expected by Raoult’s Law. As the bonds between distinct components are weaker than those in pure substances.
What shows Negative Deviation from Raoult’s Law?
When the intermolecular interactions between the components of a solution are greater than the intermolecular forces in the pure components, the solution exhibits a negative deviation from Raoult’s Law.
As a result, the solution’s vapor pressure is lower than what Raoult’s Law assumed.

What is Positive and Negative Deviation of Raoult’s Law?
- Positive Deviation: When the total vapour pressure of the solution exceeds the corresponding vapour pressure in the case of an ideal solution, there is a positive deviation from Raoult’s law.
- Negative Deviation: When the total vapour pressure of the solution is lower than the comparable vapour pressure in the case of the ideal solution, there is a negative deviation from Raoult’s law.
What is the difference between Positive and Negative Deviation Class 12?
| POSITIVE DEVIATION | NEGATIVE DEVIATION |
| The actual vapor pressure of the solution is greater than what is expected by Raoult’s Law. | The actual vapor pressure of the solution is less than what is expected by Raoult’s Law. |
| Compared to the forces within pure components, the intermolecular forces in a solution between distinct molecules are weaker. | Compared to the forces within pure components, the intermolecular forces in a solution between distinct molecules are stronger. |
| It forms maximum boiling azeotropes. | It forms minimum boiling azeotropes. |
| When combining elements that don’t interact significantly, positive deviation frequently happens. | When two components interact strongly, a negative deviation is produced. |
What is an Example of Positive Deviation and Negative Deviation?
| EXAMPLE OF POSITIVE DEVIATION | EXAMPLE OF NEGATIVE DEVIATION |
| Acetone-chloroform solution is a prominent example of positive deviation. These chemicals have weaker interactions in solution than in their pure states, resulting in a higher vapour pressure. | The ethanol solution in water is a typical example of a negative deviation. The ethanol-water strong hydrogen bond causes a lower-than-expected vapour pressure. |

Why HCl and H2O Show Negative Deviation?
When Hydrochloric acid or HCl and H2O or water combine, they generate strong hydrogen bonds and ion-dipole interactions, causing a negative deviation from Raoult’s law.
HCl is a polar molecule. It reacts with H2O or water, which is a highly polar solvent, by means of a strong interactions between hydrogen bonds and ion-dipole forces.
Raoult’s Law predicts a higher vapor pressure, yet this interaction produces a more organized and more efficient structure than its pure components.
What is the Raoult’s Law Class 12?
The partial vapour pressure of a solvent in a solution is equal to the vapour pressure of the pure solvent multiplied by its mole fraction in the solution, according to Raoult’s law.
What is Positive and Negative Deviation from Ideal Gas?
Positive and Negative Deviation for ideal gas is defined as:
Positive Deviation from Ideal Gas
The real gas behaves differently than the ideal gas law predicts, with either a higher pressure or lower volume.
Gas molecules occupy a substantial amount as compared to the container’s volume. In simpler terms, the finite size of gas molecules limits the readily available volume for movement.
The repelling interactions between gas molecules become more important. Which leads to higher pressure than the ideal prediction.
As for example, at high pressures while maintaining low temperatures, gases such as hydrogen or helium can exhibit positive deviations resulting from non-negligible repulsive forces between molecules.
Negative Deviation from Ideal Gas
The real gas behaves differently than the ideal gas law predicts, with either a lower pressure or higher volume.
The attracting interactions between gas molecules become more important. Which leads to lower pressure than the ideal prediction.
At reasonable pressures and temperatures, gases such as ammonia or carbon dioxide can exhibit negative deviations. Because the attraction forces between molecules diminish the pressure applied on the container.
What is Negative Deviation from Raoult’s Law Entropy?
Entropy is a measure of disorder or unpredictability in a system. When dealing with the negative deviation from Raoult’s Law, entropy is an important factor.
The entropy of the solution often reduces because of the creation of strong interactions between molecules, ultimately resulting in a more organized system.
Because of the more intense interactions and lower entropy in the solution, the actual vapor pressure is lower compared to that which is predicted by Raoult’s Law.
What is Positive Deviation from Raoult’s Law Equation?
When a solution deviates positively from Raoult’s Law, it means that its actual vapour pressure is higher than what the law anticipated.
The activity coefficients of the solution’s constituent components are frequently used to explain the deviation.
Raoult’s Law Formula : Raoult’s Law Equation Class 12
Raoult’s Law Equation:
“Psolution = AxPx + AYPY“
The solution’s total vapour pressure is denoted by Psolution.
The mole fractions of components X and Y are denoted by Ax and AY.
The vapour pressures of pure components A and B are denoted by Px and PY.

What is an Example of Positively Deviated Solution?
A typical example of a solution that deviates positively from Raoult’s Law is acetone and chloroform mixed together.
The combination of acetone and chloroform is a wellknown example of a solution that shows positive departure from Raoult’s Law.
n comparison to their pure states, the intermolecular interactions between acetone and chloroform are weaker in solution.
This results from the fact that neither component interacts substantially with the other as well as forms the different forms of intermolecular forces.
Because the compound is less stable and the molecules escape into the vapour phase more easily than what is estimated by Raoult’s Law, the actual vapour pressure of the mixture of acetone and chloroform solution is higher than that of the predicted solution.
As an outcome, a solution exhibiting a vapor pressure that is higher than the expected vapor pressure is produced, which results in positive deviation.
What is Mean By Positive Deviation?
Which Liquid Shows Positive Deviation from Raoult’s Law?
Solution of mixture of acetone and ethanol shows positive deviation from Raoult’s law.
What is an Example of Non Ideal Solution Showing Positive Deviation from Raoult’s Law?
A mixture of solution of acetone and ethanol are a common example of a non-ideal solution that deviates positively from Raoult’s Law.
What Type of Azeotrope is Formed by Positive Deviation from Raoult’s Law?
A minimum boiling azeotrope is one which forms in response to a positive deviation from Raoult’s Law.
What is an Example of Positively Charged Solution?
A solution containing sodium chloride and water, also known as NaCl in water, is a perfect example of a solution where the solute ions are charged positively.
This solution contains positively charged sodium ions (Na⁺).
Is Ethanol and Water Positive Deviation?
‘Yes’. A mixture of ethanol and water deviates positively from Raoult’s Law.
The ethanol-water azeotrope has a higher vapor pressure than would be predicted if the solution perfectly adhered to Raoult’s Law and boils at a temperature lower than that of either pure ethanol or pure water.
What is Positive Deviation from Raoult’s Law Boiling Point?
Positive deviation results in a lower boiling point than the ideal situation that Raoult’s Law suggests; for some compositions, this can be represented as a minimal boiling azeotrope.
Why Positive Deviation Shows Minimum Boiling Point?
There is no minimal boiling point indicated by positive deviation from Raoult’s Law. Rather, it usually causes a solution to boil at a greater temperature than what Raoult’s Law might’ve predicted.
Why Positive Deviation Shows Minimum Boiling Azeotrope?
A minimum boiling azeotrope may occur as a result of a positive deviation from Raoult’s rule and the interaction of intermolecular forces and vapor-liquid equilibrium.
A mixture that boils at a constant temperature and has the same composition in its liquid and vapor stages is known as an azeotrope.
Positive deviation in a solution indicates that the vapor pressure is higher than ideal, which may cause the vapor pressure to peak at a certain composition.
At a particular composition where the vapor pressure is the highest, the boiling point of a solution with positive deviation may be lesser than that of the components that are pure.
This leads to a minimum boiling azeotrope as an outcome.
As the boiling point is lowest at this temperature, the combination distills without changing its composition.
Positive deviation from Raoult’s Law Graph
The typical plot for a graph displaying a positive deviation from Raoult’s Law would look like this:
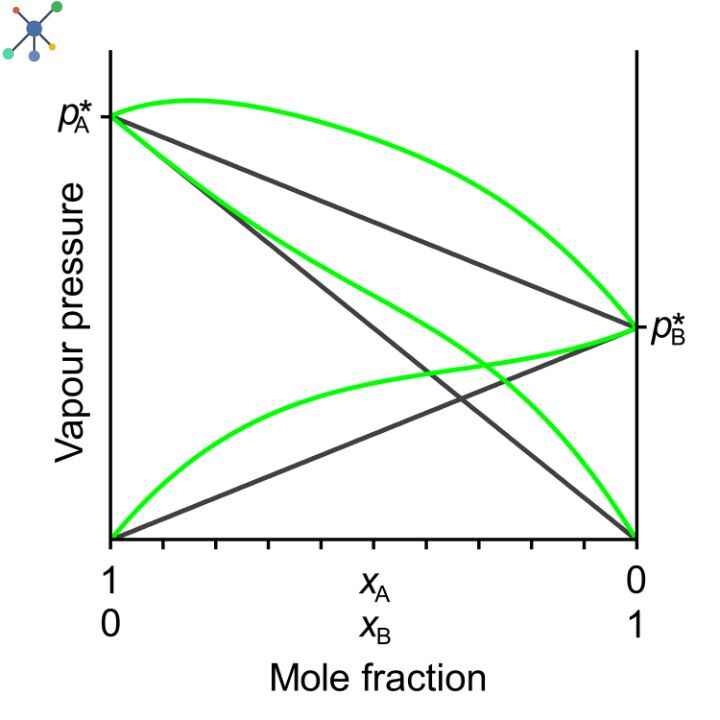
Where, the X axis represents the mole fraction of one component.
And, the Y axis represents the vapor pressure of the solution.
If you find this article on ‘Positive Deviation From RAOULT’S LAW‘ help. Please share this article and leave a comment if you have any doubt regarding this post. Thank you!
